Salient Features
- Compact Robust Unit
- Simple Wear Adjustment
- High Operating Frequency with manual release provision.
- Coil with class 'F' insulation
- All metal parts are Rust Protected.
- Two Friction Surfaces
- Low Power Requirement
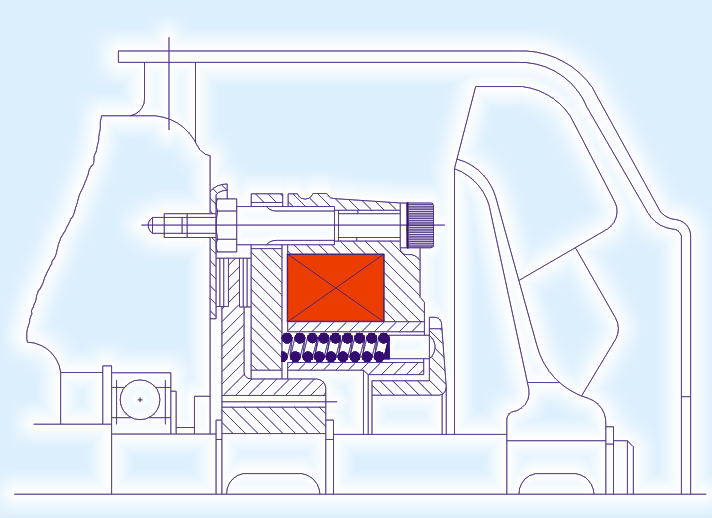
Working of EFSB
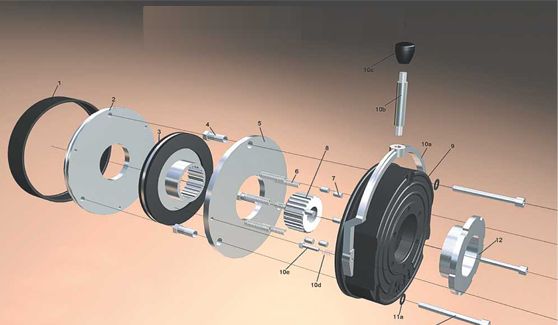
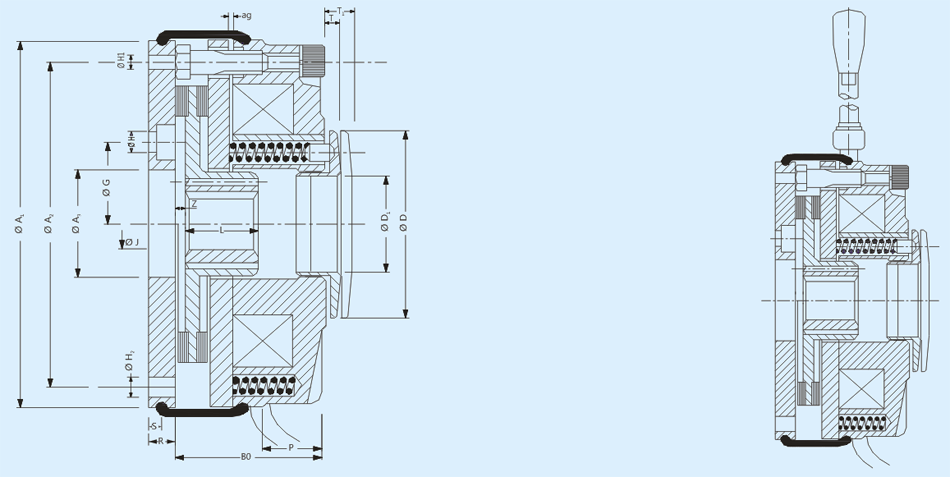
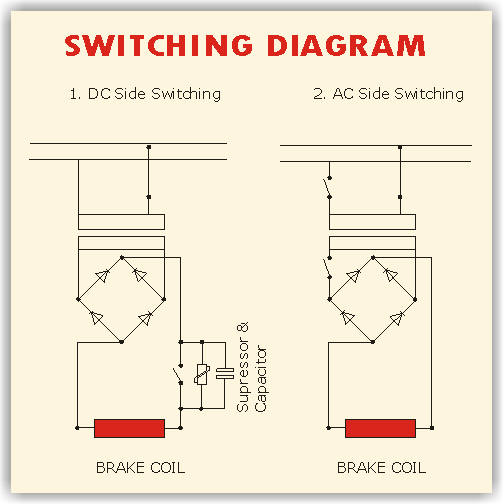
The braking torque in EXCEL spring loaded fail safe brake is generated by several compression springs (6) whose axial spring force presses the armature plate (5)against the rotor (3)which in turn is pushed against the mounting flange(2). On applying direct current power supply to the coil (9) magnetic field is produced, which pulls the armature plate over the airgap towards the "STATOR" against the spring force and the rotor is free to rotate and hence brake is released.The brakes are provided with manual hand release assembly and can be used for releasing the brake in case of power failure.
Description
- 1. Dust Protective Ring
- 2. Flange
- 3. Rotor
- 4. Tubular Bush
- 5. Armature Plate
- 6. Compression Spring
- 7. Compression Parts
- 8. Hub
- 9. Outer Pole
- 10. a- Handle
- b- H.R. Lever
- c- Knob
- d- H.R. Spring
- e- H.R. Bolt
- 11. a- Spring Washer
- b- Mounting Bolt
- 12. Torque Adjustment Nut